In today’s fast-changing IT world, keeping networks safe is key. The Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a top choice for managing who gets in and what they can do. It helps keep important data and resources safe in an organization’s network.
This article will explore how RADIUS works. We’ll look at its basics, main parts, and how it uses different protocols and methods. We’ll also see how RADIUS servers boost network security and how they communicate with clients. Plus, we’ll share tips for using RADIUS in big networks and ways to tackle common security issues.
Key Takeaways
- RADIUS authentication is a widely adopted protocol for secure access control and user verification in enterprise networks.
- RADIUS architecture comprises key components, including RADIUS clients, RADIUS servers, and authentication protocols, that work together to manage authentication and authorization processes.
- RADIUS servers play a vital role in enhancing network security by validating user credentials and enforcing access policies.
- The RADIUS client-server communication process involves a series of authentication requests and responses, culminating in an access decision and authorization.
- Implementing RADIUS authentication best practices and addressing security challenges is crucial for maintaining a robust and secure enterprise network infrastructure.
Understanding RADIUS Authentication Fundamentals
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a key part of network security. It’s a widely used AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) framework. It helps secure user access to enterprise networks.
Key Components of RADIUS Architecture
The RADIUS system has three main parts:
- RADIUS server: This is the core that handles all authentication, authorization, and accounting requests.
- RADIUS client: These are network devices like routers and switches that send requests to the RADIUS server.
- Shared secret: A secret key that keeps communication between the client and server safe.
Authentication Protocols and Methods
RADIUS uses different authentication methods:
- EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol): It’s flexible and supports many authentication ways.
- CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol): Uses a challenge-response for user verification.
- PAP (Password Authentication Protocol): A simple method that uses usernames and passwords.
The choice of method depends on the network’s security needs and the devices’ capabilities.
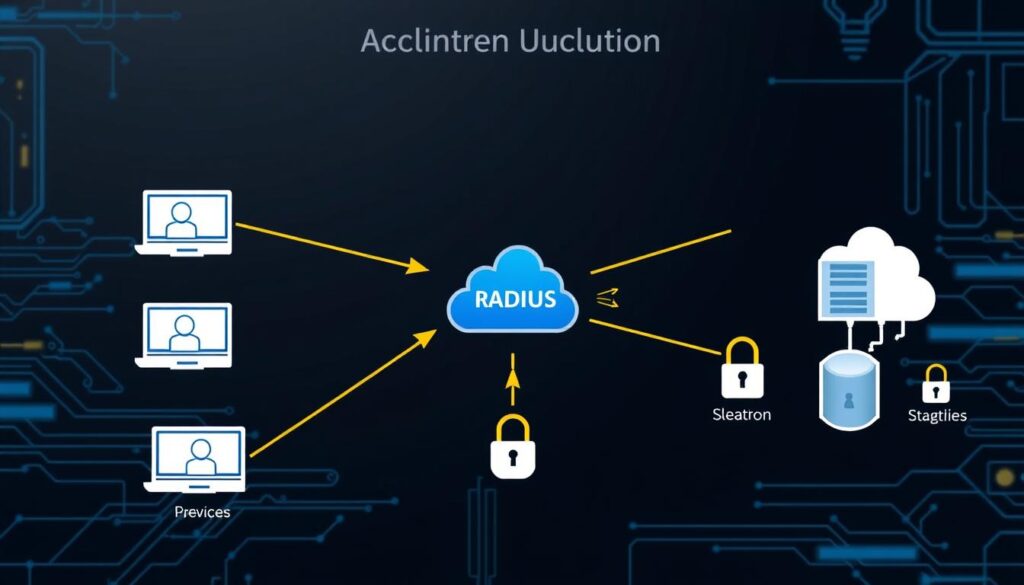
Basic RADIUS Communication Flow
The RADIUS flow includes these steps:
- A network device gets an authentication request from a user.
- The device sends the request to the RADIUS server with the user’s details.
- The server checks the user’s credentials and decides on access.
- The device then allows or blocks the user’s access based on the server’s decision.
The Role of RADIUS Servers in Network Security
In today’s fast-changing business world, RADIUS servers are key to better security. They control who gets in and what they can do. This helps keep the network safe and running smoothly.
RADIUS makes it easier to manage who can get into the network. Instead of dealing with many different login systems, RADIUS does it all in one place. This makes it easier to keep the network safe from outside threats.
RADIUS also lets companies set up strict rules for who can do what. This means they can keep important parts of the network safe from unauthorized access. It’s a big help in keeping the network secure.
Another important thing RADIUS does is keep a detailed record of everything that happens on the network. This helps find and fix problems fast. It also helps companies follow the rules they need to.
To wrap it up, RADIUS servers are very important for keeping networks safe. They help manage who gets in, what they can do, and keep a record of everything. This makes networks more secure and helps protect important information.

How Does RADIUS Authentication Work for Enterprise Networks?
The RADIUS protocol is key to keeping enterprise networks safe. It works by managing who gets to access the network. This includes understanding how the client and server talk to each other, the steps to check if someone is allowed in, and what access they get.
RADIUS Client-Server Communication Process
The RADIUS system starts with a client-server chat. When someone tries to get into the network, the client (like a VPN server) sends a request to the server. This request has details about the user and what they need to get into the network.
Authentication Request and Response Cycle
The server checks the request against a database. If it’s okay, the server tells the client they can get in. If not, they’re told they can’t. This is how the server decides who gets to use the network.
Access Decision and Authorization
After getting the server’s answer, the client decides what to do next. If they’re allowed in, they might get more details about what they can do. This could be what websites they can visit or how much data they can use.
| RADIUS Protocol Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication Request | The request sent by the RADIUS client to the RADIUS server, containing user credentials and other relevant information. |
| Access-Accept | The response from the RADIUS server indicating that the user is authorized to access the network. |
| Access-Reject | The response from the RADIUS server denying the user’s access to the network. |
| RADIUS Attributes | Additional information included in the RADIUS request and response, such as user profiles, network policies, and authorization details. |
RADIUS Implementation Best Practices
Setting up RADIUS authentication in enterprise networks needs a smart plan. Let’s look at some top tips for a strong and safe RADIUS setup.
Configure RADIUS Server Redundancy
It’s key to avoid service outages by having RADIUS server redundancy. Use multiple RADIUS servers in a failover setup. This way, users can keep logging in smoothly, even if one server goes down.
Prioritize RADIUS Server Encryption
Encryption is a must for RADIUS authentication. Make sure the link between RADIUS clients and servers is secure. Use RADIUS over TLS (RADIUS/TLS) or RADIUS over DTLS (RADIUS/DTLS). This keeps user data safe from hackers.
Integrate RADIUS with Network Access Control
Boost security by linking your RADIUS setup with a strong network access control (NAC) system. This lets you set VLAN assignment and role-based access control rules. It makes sure users and devices can only get to what they’re allowed to.
By sticking to these guidelines, you’ll have a RADIUS system that’s safe, has backup options, and works well with your network.
Common RADIUS Security Challenges and Solutions
The RADIUS protocol is key for network authentication in enterprises. It faces many security challenges. It’s vital to tackle these issues and use strong solutions to keep your network safe.
Addressing Authentication Vulnerabilities
Weak passwords are a big worry with RADIUS. To fix this, set up strict password policies. This means passwords must be long, complex, and changed often. Adding multi-factor authentication also boosts security.
Preventing RADIUS Server Attacks
RADIUS servers can be hit by DDoS protection and unauthorized access. Use network segmentation, firewalls, and log monitoring to stop these attacks. Keeping an eye on RADIUS server logs is key to spotting and stopping trouble.
Troubleshooting Authentication Issues
When RADIUS authentication goes wrong, having a solid troubleshooting plan is crucial. Check client settings, user info, and server logs for problems. Good RADIUS security documentation and a clear incident response plan help solve issues fast.
| Security Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Weak password policies | Enforce strong password requirements, including minimum length, complexity, and regular changes. Implement multi-factor authentication. |
| RADIUS server attacks | Ensure proper network segmentation, implement firewalls, and monitor server logs for suspicious activity. Maintain comprehensive RADIUS security documentation and incident response plan. |
| Authentication issues | Review client configurations, verify user credentials, and examine server logs for errors or anomalies. Establish a well-defined troubleshooting process. |
Conclusion
The RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) protocol is key for keeping enterprise networks safe. It offers many benefits like strong user checks, one place for access control, and better network security.
We’ve looked at how RADIUS works, its main parts, and the different ways it authenticates users. We’ve also seen how RADIUS servers protect networks, manage user access, and fight off threats.
The future of network security looks bright, with RADIUS leading the way. As cyber threats grow, RADIUS will help keep networks safe. By using RADIUS, companies can protect their networks, follow rules, and stay strong against new dangers. This will help them succeed in the digital world.
