Introduction of DOCSIS
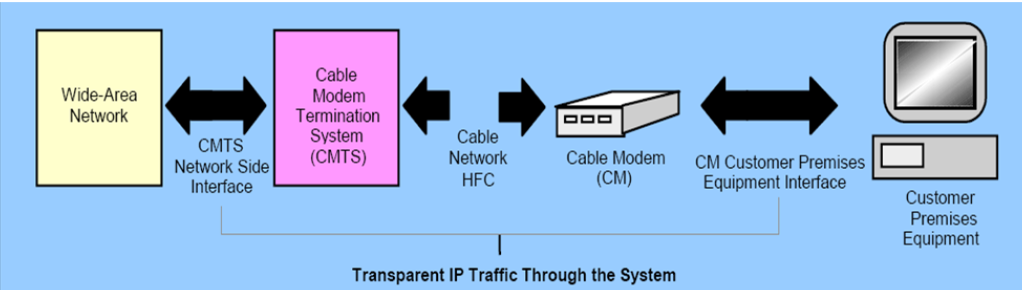
In this blog I will cover what is DOCSIS technology. The cable modem industry adheres to a set of standardized specifications known as DOCSIS, which stands for Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification. DOCSIS defines the protocols and requirements that ensure interoperability between cable modems and the infrastructure provided by different ISPs.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe DOCSIS System consists of:
- Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS)
- Cable Network(HFC)
- Cable Modem (CM)
What is DOCSIS Cable Modem
The principle function of the DOCSIS Cable Modem System is to transmit Internet Protocol (IP) packets transparently between internet service provider (ISP) and the subscriber premise location. One of the distinctive characteristics of cable modems is their use of both downstream and upstream channels for data transmission. Downstream channels carry data from the internet to the user, delivering content such as web pages, videos, and download. Upstream channels, on the other hand, facilitate the transmission of user-generated data, such as requests, uploads, and other interactive communication.
Over the years, DOCSIS has seen multiple versions, each introducing improvements in terms of data transfer speeds, security features, and overall performance.
What is DOCSIS CMTS
A Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) is a sophisticated networking device that serves as the gateway between cable modems and the Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) network infrastructure. In the realm of cable broadband services, the CMTS plays a pivotal role in managing, controlling, and optimizing the flow of data between the cable modems at the user end and the broader Internet backbone. the CMTS consists of a downstream module, an upstream module, and a control and management module.
DOCSIS Service Goals
- Increasing channel capacity
- Enhancing network security
- Expanding addressability of network elements
- Deploying new service offerings
DOCSIS technology has indeed come a long way since its evolution, transforming the digital landscape and redefining our expectations of internet connectivity. DOCSIS has consistently adapted to the changing needs of consumers and the technological advancements of the era. Each version of DOCSIS (1.0, .1.1, 2.0, 3.0, 3.1) brings forth new capabilities, higher speeds, and enhanced performance.
Frequently asked questions:
- What is the difference between CM and CMTS?
CMTS is networking device that serves as the gateway between cable modems and the Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) network infrastructure. While CM serves as the bridge between CMTS and the end-user’s devices.
- What is HFC?
HFC stands for hybrid fiber coaxial which is coaxial cable network. A cable modem is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via RF channels on a hybrid fiber coaxial (HFC)
- What are different version of DOCSIS available?
Different versions of DOCSIS Are DOCSIS 1.0, DOCSIS 1.1, DOCSIS 2.0, DOCSIS 3.0, DOCSIS 4.0
